Introduction to Active Investing
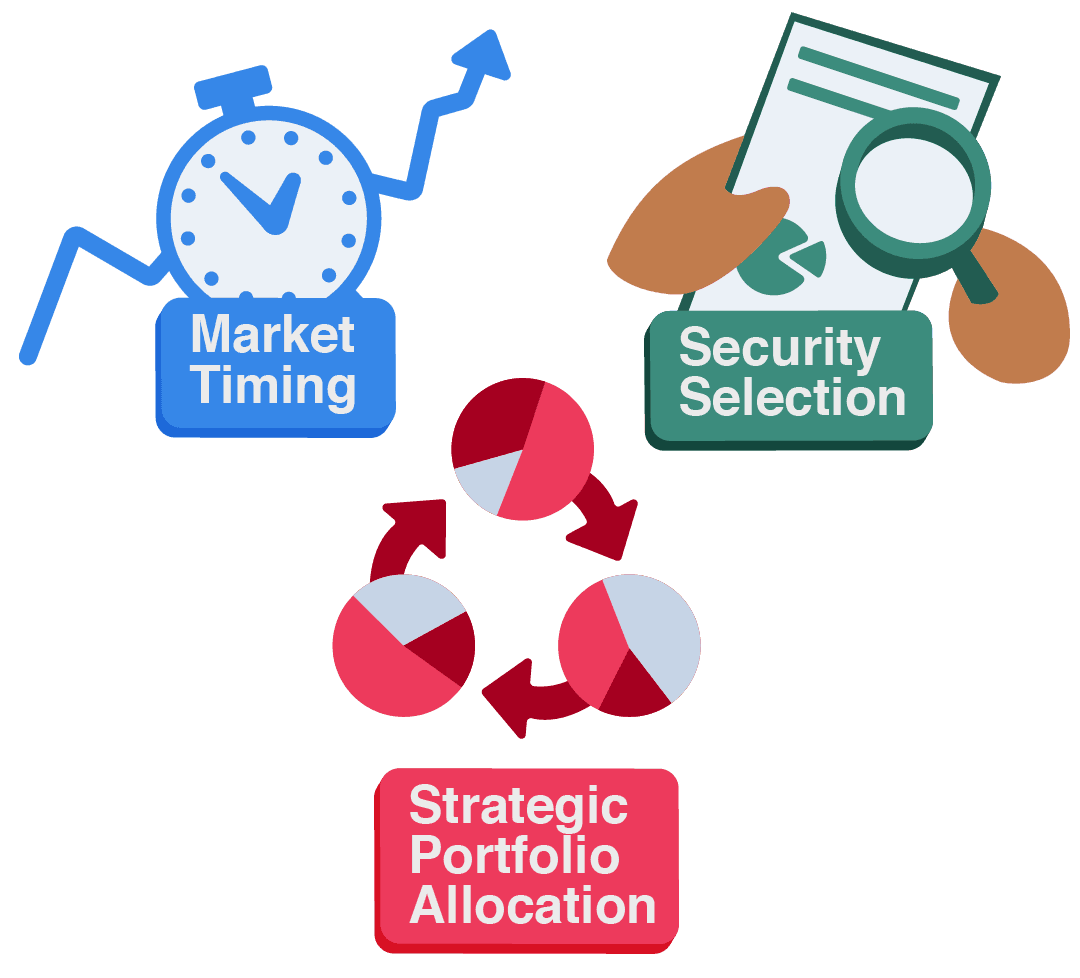
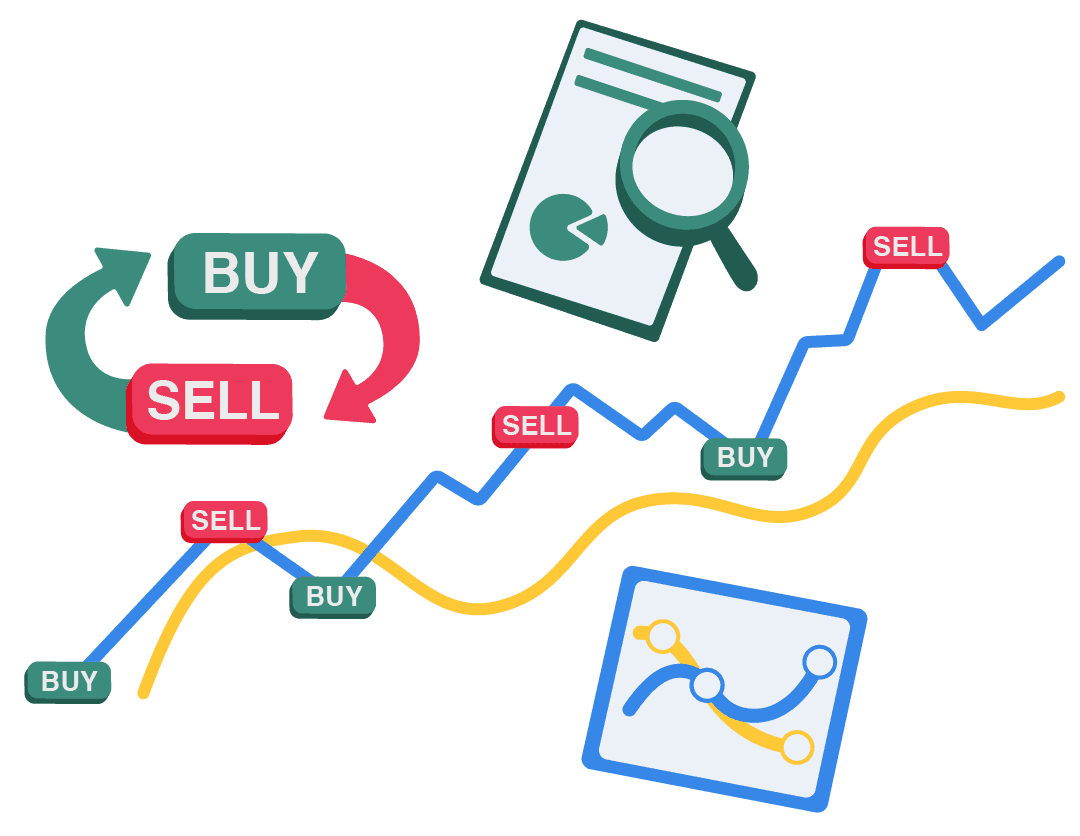
Active investing involves regularly selecting, buying, and selling assets to outperform a benchmark index.
Unlike passive approaches that track an index over the long term, active investors study market trends, analyze company reports, and adjust their holdings based on new information gathered.
This approach aims for above-average returns through informed decisions, adapting quickly to shifting conditions rather than simply mirroring the broader market.