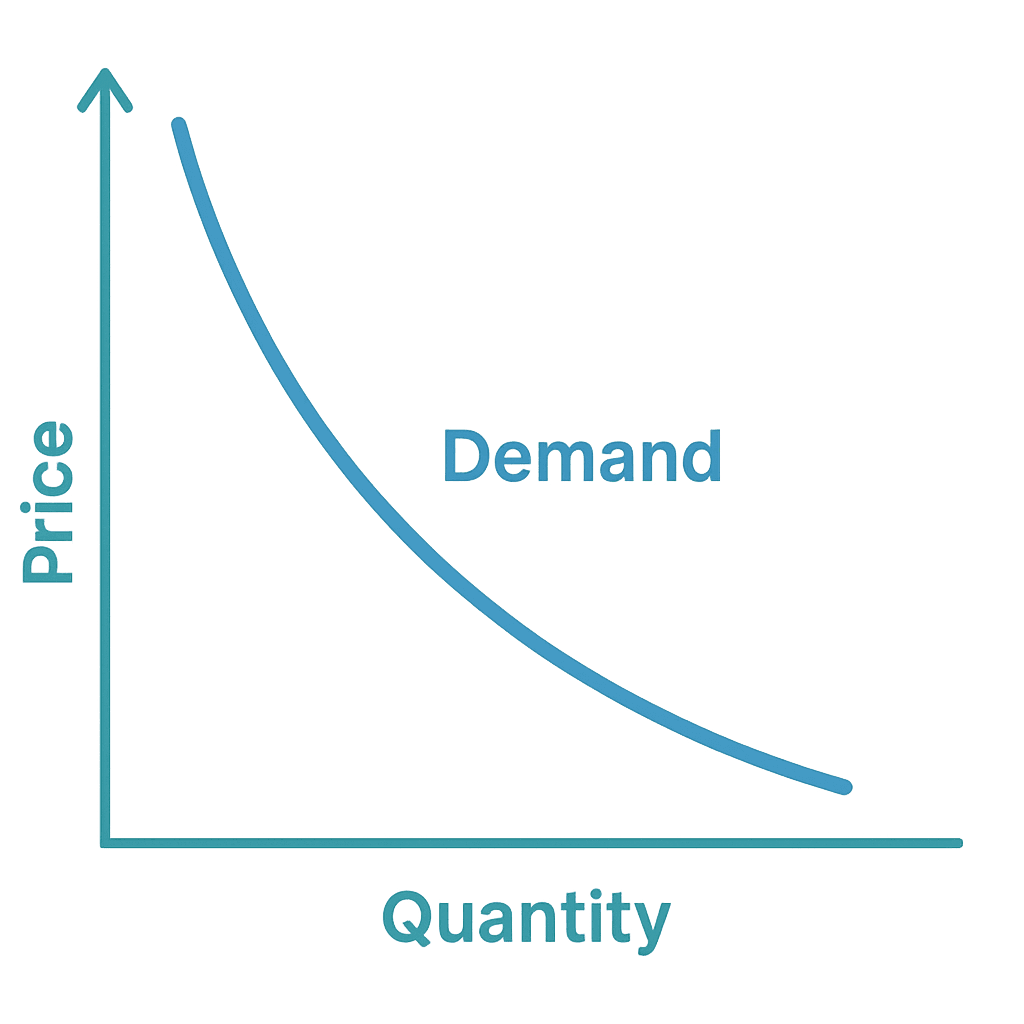
Introduction to Demand
Gain a deeper understanding of the world by exploring how supply and demand influence both the economy and daily life, shaping everything from market trends to personal decisions.
These fundamental concepts form the backbone of economic theory, influencing everything from the price of groceries to the stock market.
Understanding supply and demand helps us make informed decisions, anticipate market trends, and grasp the broader economic forces at play.